Some ISP's that offer free wifi will not allow you to ssh. To get around this you can set your ssh server to use another port like 8080.
For Fedora 30
1) sudo vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Change
#Port 22
to
Port 22
Port 8080
# This allows two ports to connect to ssh
2) Update selinux to allow ssh on port 8080
sudo semanage port -m -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 8080
If you use -a you will get an error like
ValueError: Port tcp/8080 already defined
If you -d you will get another error like
ValueError: Port tcp/8080 is defined in policy, cannot be deleted
Use this to check:
sudo semanage port -l | grep 8080
http_cache_port_t tcp 8080, 8118, 8123, 10001-10010
ssh_port_t tcp 8080, 22
Sunday, November 17, 2019
Saturday, August 17, 2019
Create an interface array consisting of a generic struct type in golang
I was looking at how to get a result set from a golang sql query. It seemed that a lot of the examples explicitly defined the fields or declared a struct that are passed into the Scan() method such as:
var id int
var name string
err = rows.Scan(&id, &name)
// or
row = MyStruct{}
err = rows.Scan(&row.Id, &row.Name)
This seemed like a lot of repetition if every query required this logic. My next thought was to see if I could pass in a struct, use reflect to obtain the fields and return a slice of values.
Here are two examples, the first one uses uses append and requires type assertion to access the fields. The second example uses reflect.append and each field can be accessed directly from the element.
Note: Additional checks should be added, such as making sure the address of the object is passed in.
First
Second
Output (same for both)
var id int
var name string
err = rows.Scan(&id, &name)
// or
row = MyStruct{}
err = rows.Scan(&row.Id, &row.Name)
This seemed like a lot of repetition if every query required this logic. My next thought was to see if I could pass in a struct, use reflect to obtain the fields and return a slice of values.
Here are two examples, the first one uses uses append and requires type assertion to access the fields. The second example uses reflect.append and each field can be accessed directly from the element.
Note: Additional checks should be added, such as making sure the address of the object is passed in.
First
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
type MyStruct struct {
Id int
Name string
}
func main() {
me := MyStruct{}
result := doIt(&me)
for _, v := range result {
fmt.Printf("%d %s\n", v.(MyStruct).Id, v.(MyStruct).Name)
}
}
func doIt(genericStruct interface{}) []interface{} {
params := []interface{}{}
var myStruct reflect.Value
structType := reflect.TypeOf(genericStruct).Elem()
// First Element
myStruct = reflect.New(structType).Elem()
myStruct.FieldByName("Id").SetInt(1)
myStruct.FieldByName("Name").SetString("one")
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", myStruct)
params = append(params, myStruct.Interface())
// Second Element
myStruct = reflect.New(structType).Elem()
myStruct.FieldByName("Id").SetInt(2)
myStruct.FieldByName("Name").SetString("two")
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", myStruct)
params = append(params, myStruct.Interface())
return params
}
Second
package main
import (
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
type MyStruct struct {
Id int
Name string
}
func main() {
myStruct := []MyStruct{}
doIt(&myStruct)
for _, v := range myStruct {
fmt.Printf("%d %s\n", v.Id, v.Name)
}
}
func doIt(genericStructArray interface{}) {
var myStruct reflect.Value
genericValue := reflect.ValueOf(genericStructArray).Elem()
genericType := genericValue.Type().Elem()
// First Element
myStruct = reflect.New(genericType).Elem()
myStruct.FieldByName("Id").SetInt(1)
myStruct.FieldByName("Name").SetString("one")
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", myStruct)
genericValue.Set(reflect.Append(genericValue, myStruct))
// Second Element
myStruct = reflect.New(genericType).Elem()
myStruct.FieldByName("Id").SetInt(2)
myStruct.FieldByName("Name").SetString("two")
fmt.Printf("%#v\n", myStruct)
genericValue.Set(reflect.Append(genericValue, myStruct))
}
Output (same for both)
main.MyStruct{Id:5, Name:"one"}
main.MyStruct{Id:2, Name:"two"}
5 one
2 two
Saturday, June 8, 2019
Learning middleware patterns in Golang
Middlewares are often applied using a wrapping a method wrapping pattern (chain of responsibility design pattern). To better understand how to do this in golang, I've started with the Handler interface and created a HandlerFunc that mimics the HandlerFunc in https://golang.org/src/net/http/server.go except I've replaced the args with (context string). This allowed me to trace the order that middlewares access the current context.
func (r *Request) Context() context.Context
Some useful links that helped guide me.
https://www.calhoun.io/why-cant-i-pass-this-function-as-an-http-handler/
https://www.alexedwards.net/blog/making-and-using-middleware
https://github.com/justinas/alice Ended with an implementation that resembles this. Thx!
Update July 2019: Middleware args changed to Handler instead of HandlerFunc
func (r *Request) Context() context.Context
Some useful links that helped guide me.
https://www.calhoun.io/why-cant-i-pass-this-function-as-an-http-handler/
https://www.alexedwards.net/blog/making-and-using-middleware
https://github.com/justinas/alice Ended with an implementation that resembles this. Thx!
Update July 2019: Middleware args changed to Handler instead of HandlerFunc
package main
import "fmt"
// HandlerFunc, ServeHTTP match the go standard libs except
// (w ResponseWriter, r *Request) has been replaced by (context string).
// We treat this as a buffer that we can read from add values to.
// Analagous to reading GET/POST args from Request and adding
// Information to Request.context()
// https://golang.org/src/net/http/server.go
// This implements Handler interface because it matches signature, meaning it has a
// ServerHTTP method with the same argument types
type Handler interface {
ServeHTTP(context string)
}
type HandlerFunc func(context string)
func (f HandlerFunc) ServeHTTP(context string) {
f(context)
}
func baseHandler(h Handler) Handler {
fmt.Println("Before return baseHandler")
return HandlerFunc(func(context string) {
fmt.Println("Before baseHandler")
context = context + " base"
h.ServeHTTP(context) // call ServeHTTP on the original handler
fmt.Println("After baseHandler")
})
}
func first(h Handler) Handler {
fmt.Println("Before return first")
return HandlerFunc(func(context string) {
fmt.Println("Before first")
context = context + " first"
h.ServeHTTP(context) // call ServeHTTP on the original handler
fmt.Println("After first")
})
}
func second(h Handler) Handler {
fmt.Println("Before return second")
return HandlerFunc(func(context string) {
fmt.Println("Before second")
context = context + " second"
h.ServeHTTP(context) // call ServeHTTP on the original handler
fmt.Println("After second")
})
}
func IndexEndPoint(s string) {
fmt.Println("Index EndPoint: ", s)
}
type Middleware func(Handler) Handler
type MiddlewareStack struct {
middlewares []Middleware
}
func NewMiddlewareStack(middlewares ...Middleware) MiddlewareStack {
return MiddlewareStack{middlewares: middlewares}
}
// The middleware wrap pattern eg. second(first(baseHandler(IndexEndPoint))
// means you need to find the deepest method and work backwards -
// baseHandler, then first, then second.
// This implementation stores the middlewares in an array and can mutate the
// values beginning with the lowest to highest index; which has some
// readability benefits.
func (ms *MiddlewareStack) EndPoint(endPoint HandlerFunc) Handler {
var h Handler
// first middlware in array can access the context first
for i := len(ms.middlewares) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
mw := ms.middlewares[i]
// for _, mw := range ms.middlewares {
if h == nil {
h = mw(endPoint)
} else {
h = mw(h)
}
}
return h
}
func main() {
// middleware function wrapping
// Output: Index EndPoint: start second first base
f := second(first(baseHandler(HandlerFunc(IndexEndPoint))))
f.ServeHTTP("start")
/*
// array of middleware
// Another version of above, but storing in an array
middleWares := []MiddleWare{baseHandler, first, second}
var hFunc HandlerFunc
for _, mw := range middleWares {
if hFunc == nil {
hFunc = mw(IndexEndPoint)
} else {
hFunc = mw(hFunc)
}
}
hFunc.ServeHTTP("start")
*/
// middleware struct
// Index EndPoint: start base first second
middlewareStack := NewMiddlewareStack(baseHandler, first, second)
hFunc := middlewareStack.EndPoint(IndexEndPoint)
hFunc.ServeHTTP("start")
}
Thursday, November 16, 2017
Firefox 57 and lost some shortcuts on mac
There was an old plugin called Customizeable Shortcuts that hadn't been updated for while and was not usable with Firefox 57. I was using it to remap the 'search location bar' shortcut.
Since I already use karabiner to remap some modifier keys for macos, it might be able to use it instead of waiting for a new firefox shortcut addon.
Note: If you're confused by the left_option/left_command it's cause I've first remap left_command to left_option.
1) Have a look at some of the examples for karabiner shortcuts
https://pqrs.org/osx/karabiner/complex_modifications/#key_specific
2) Create a json and take note of the path
{
"title": "Firefox command-d search location",
"rules": [
{
"description": "command-d search location",
"manipulators": [
{
"type": "basic",
"from": {
"key_code": "d",
"modifiers": {
"mandatory": ["left_option"],
"optional": ["any"]
}
},
"to": [
{
"key_code": "l",
"modifiers": [
"left_command"
]
}
],
"conditions": [
{
"type": "frontmost_application_if",
"bundle_identifiers": [
"^org\\.mozilla\\.firefox"
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
I saved this to my desktop with the name firefox-command-d.json
What is going on? frontmost_application_if only runs the above shortcuts if it's the app focused.
bundle_identifiers is your app id that you can find in the plist.
3) Now run enter this in the url bar in firefox: karabiner://karabiner/assets/complex_modifications/import?url=file:///Users//Desktop/firefox-command-d.json
Enable this and you have your remap.
Since I already use karabiner to remap some modifier keys for macos, it might be able to use it instead of waiting for a new firefox shortcut addon.
Note: If you're confused by the left_option/left_command it's cause I've first remap left_command to left_option.
1) Have a look at some of the examples for karabiner shortcuts
https://pqrs.org/osx/karabiner/complex_modifications/#key_specific
2) Create a json and take note of the path
{
"title": "Firefox command-d search location",
"rules": [
{
"description": "command-d search location",
"manipulators": [
{
"type": "basic",
"from": {
"key_code": "d",
"modifiers": {
"mandatory": ["left_option"],
"optional": ["any"]
}
},
"to": [
{
"key_code": "l",
"modifiers": [
"left_command"
]
}
],
"conditions": [
{
"type": "frontmost_application_if",
"bundle_identifiers": [
"^org\\.mozilla\\.firefox"
]
}
]
}
]
}
]
}
I saved this to my desktop with the name firefox-command-d.json
What is going on? frontmost_application_if only runs the above shortcuts if it's the app focused.
bundle_identifiers is your app id that you can find in the plist.
3) Now run enter this in the url bar in firefox: karabiner://karabiner/assets/complex_modifications/import?url=file:///Users/
Enable this and you have your remap.
Friday, January 6, 2017
Blurry Font in Firefox after updating to Linux Fedora 25
I recently did a clean update of fedora and found the font to render quite blurry.
What I found out:
1) gnome-tweak-tool font settings do not work. At the time of the post any of the font settings did not make a difference.
2) You may start trying to use font-tweak-tool or font-manager. Be aware that these may create font config files in your ~/ or in ~/.config
These may need to be deleted so that your gnome settings take precedence.
Note: I've installed microsoft and ubuntu fonts for linux.
So what's the fix?
a) Go to Settings > Fonts and change the settings here to Anti Aliasing: rgba and Hinting: full
At this point your terminal should look good.
b) For me, firefox and sublime text had bad looking fonts.
There's a directory in /etc/fonts/conf.d that controls some additional font rendering. It's odd that there's no GUI to modify this directly.
sudo ln -s /usr/share/fontconfig/conf.avail/10-hinting-full.conf /etc/fonts/conf.d/
sudo rm /usr/share/fontconfig/conf.avail/10-hinting-slight.conf
Log out and Log back in and things should be clearer.
What I found out:
1) gnome-tweak-tool font settings do not work. At the time of the post any of the font settings did not make a difference.
2) You may start trying to use font-tweak-tool or font-manager. Be aware that these may create font config files in your ~/ or in ~/.config
These may need to be deleted so that your gnome settings take precedence.
Note: I've installed microsoft and ubuntu fonts for linux.
So what's the fix?
a) Go to Settings > Fonts and change the settings here to Anti Aliasing: rgba and Hinting: full
At this point your terminal should look good.
b) For me, firefox and sublime text had bad looking fonts.
There's a directory in /etc/fonts/conf.d that controls some additional font rendering. It's odd that there's no GUI to modify this directly.
sudo ln -s /usr/share/fontconfig/conf.avail/10-hinting-full.conf /etc/fonts/conf.d/
sudo rm /usr/share/fontconfig/conf.avail/10-hinting-slight.conf
Log out and Log back in and things should be clearer.
Wednesday, September 21, 2016
MacOS 10.12 sierra karibiner and seil are broken
After updating to macos sierra it seems seil and karabiner do not work any more. From the official site it looks like it will take a while before the replacement app karabiner-elements is ready for prime time.
https://github.com/tekezo/Karabiner-Elements
1) Start Karibiner and take a screen shot of your current settings. Check off 'Show enabled only'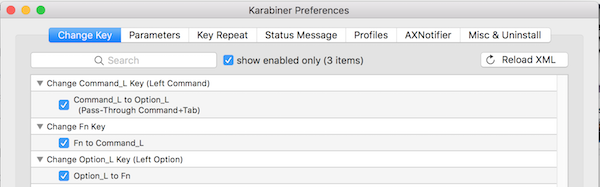
2) Uninstall seil and karabiner.
I found that macos would not shut down cleanly after this step. Like it was failing on closing a process and hanged. Seems to have went away after installing karabiner-elements.
3) Install karabiner-elements and create the file ~/.karabiner.d/configuration/karabiner.json
https://pqrs.org/latest/karabiner-elements-latest.dmg (mentioned in the above github README.md)
4) To get back my settings I added the following remaps.
{
"profiles": [
{
"name": "Default profile",
"selected": true,
"simple_modifications": {
"caps_lock": "escape",
"left_command": "left_option",
"left_option": "fn",
"fn": "left_command"
}
}
]
}
5) To get the names of keys to add to the above, you can't really use the karabiner event viewer app. I was seeing Command_L and Fn. The following file has a list of all the acceptable names. control-f for left_command and you can see other ones that might suit your needs.
https://github.com/tekezo/Karabiner-Elements/blob/master/src/share/types.hpp
Hope this helps.
https://github.com/tekezo/Karabiner-Elements
1) Start Karibiner and take a screen shot of your current settings. Check off 'Show enabled only'

2) Uninstall seil and karabiner.
I found that macos would not shut down cleanly after this step. Like it was failing on closing a process and hanged. Seems to have went away after installing karabiner-elements.
3) Install karabiner-elements and create the file ~/.karabiner.d/configuration/karabiner.json
https://pqrs.org/latest/karabiner-elements-latest.dmg (mentioned in the above github README.md)
4) To get back my settings I added the following remaps.
{
"profiles": [
{
"name": "Default profile",
"selected": true,
"simple_modifications": {
"caps_lock": "escape",
"left_command": "left_option",
"left_option": "fn",
"fn": "left_command"
}
}
]
}
5) To get the names of keys to add to the above, you can't really use the karabiner event viewer app. I was seeing Command_L and Fn. The following file has a list of all the acceptable names. control-f for left_command and you can see other ones that might suit your needs.
https://github.com/tekezo/Karabiner-Elements/blob/master/src/share/types.hpp
Hope this helps.
Saturday, March 12, 2016
Kernel Crashing after upgrading to Fedora 23
After upgrading to from fedora 22 to fedora 23, I was unable to boot into linux due to a kernel crash. I was able to load up the previous kernel from 22 to get back to desktop.
I thought it might be a bad grub config so I ran this to rebuild grub
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
This produced a lot of errors such as:
ERROR: pdc: reading /dev/sdb[Input/output error]
It looks like the initramfs could be corrupt.
Solution:
sudo dracut --regenerate-all --force
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
No errors were produced at this time.
I thought it might be a bad grub config so I ran this to rebuild grub
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
This produced a lot of errors such as:
ERROR: pdc: reading /dev/sdb[Input/output error]
It looks like the initramfs could be corrupt.
Solution:
sudo dracut --regenerate-all --force
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
No errors were produced at this time.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)